In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, one term that has gained significant prominence is "Artificial Intelligence" (AI). AI, a branch of computer science, is dedicated to creating machines and systems that mimic human intelligence and cognitive processes.
As AI technology continues to advance, it will likely become even more deeply embedded in various aspects of our routines, enhancing convenience, efficiency, and overall quality of life. Here are some common ways AI is used by us already day:
- Virtual Assistants: AI-powered virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant, and Cortana.
- Search Engines: Search engines like Google and Bing use AI algorithms to understand the context of our search queries and provide us with relevant search results.
- Social Media: AI plays a significant role in social media platforms to personalize our feeds, show us relevant content, and suggest people we might know.
- Online Shopping: AI is used in recommendation systems that analyze our shopping behavior and suggest products we might be interested in.
- Navigation Apps: Apps like Google Maps and Waze use AI to provide real-time traffic updates, calculate the fastest routes, and suggest alternative paths.
- Email Filtering: AI-driven spam filters in email services like Gmail help keep unwanted emails out of our inboxes.
- Ride-Sharing Apps: Ride-sharing apps like Uber and Lyft use AI to determine ride prices, match drivers with passengers, and optimize routes for efficiency.
- Language Translation: AI-powered translation services like Google Translate use neural networks to provide accurate translations between languages.
- Healthcare Diagnostics: AI is used in medical imaging to help doctors identify potential health issues from X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans.
- Personalized Content: Streaming platforms like Spotify and YouTube use AI to recommend music, videos, and content based on our preferences and listening/watching history.
- Fraud Detection: AI algorithms are used by financial institutions to detect unusual patterns in transactions and identify potential fraud.
- Smart Homes: Smart home devices, like thermostats and lights, use AI to learn our preferences and adjust settings accordingly for energy efficiency and convenience.
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars use AI to navigate roads, detect obstacles, and make real-time driving decisions.
- Language Processing: AI is used in speech recognition technology for voice commands and dictation, as well as in chatbots that provide customer support on websites.
- Predictive Text and Autocorrect: Your smartphone's keyboard likely uses AI to suggest words as you type and correct misspelled words.
- Weather Forecasting: Meteorologists use AI models to analyze vast amounts of weather data and make predictions about weather conditions.
- Language Learning Apps: AI-powered language learning apps adapt to your progress, offering lessons and exercises tailored to your skill level and learning pace.
- Personalized News Feeds: News platforms use AI to customize news articles and stories based on your interests and reading habits
However, all of them represent the easiest AI opportunities. As the technology continues to advance, it has been categorized into four distinct types, each representing a unique level of sophistication and capability. In this blog, we'll explore all of them: from narrow to general intelligence, their use cases, benefits, and more.
Narrow or weak AI
Narrow AI constitutes the most prevalent form of artificial intelligence that we encounter in our daily lives.
- Also known as Weak AI.
- Specialized AI.
- Task-specific AI.
- Domain-specific AI.
It is designed to perform a specific task or a set of tasks with remarkable precision and efficiency. However, its scope remains confined to predefined tasks, and it lacks the ability to exhibit true cognitive understanding.
Examples of Narrow AI can be found in various applications, such as virtual personal assistants (Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant) that assist in setting reminders, answering questions, and playing music. Additionally, recommendation systems on streaming platforms, social media algorithms, and even spam filters in email services are all manifestations of Narrow AI.
Think about Netflix or Amazon: These AI algorithms analyze user preferences and behaviors to suggest movies, products, or content that align with their interests. However, their capabilities are limited to making recommendations within their designated platforms.

General or strong AI
In contrast to Narrow AI, General AI is the holy grail of artificial intelligence – a system with human-like cognitive abilities capable of understanding, reasoning, learning, and applying knowledge across a wide array of tasks.
- Also known as Strong AI.
- Human-level AI.
- Human-like AI.
- True AI.
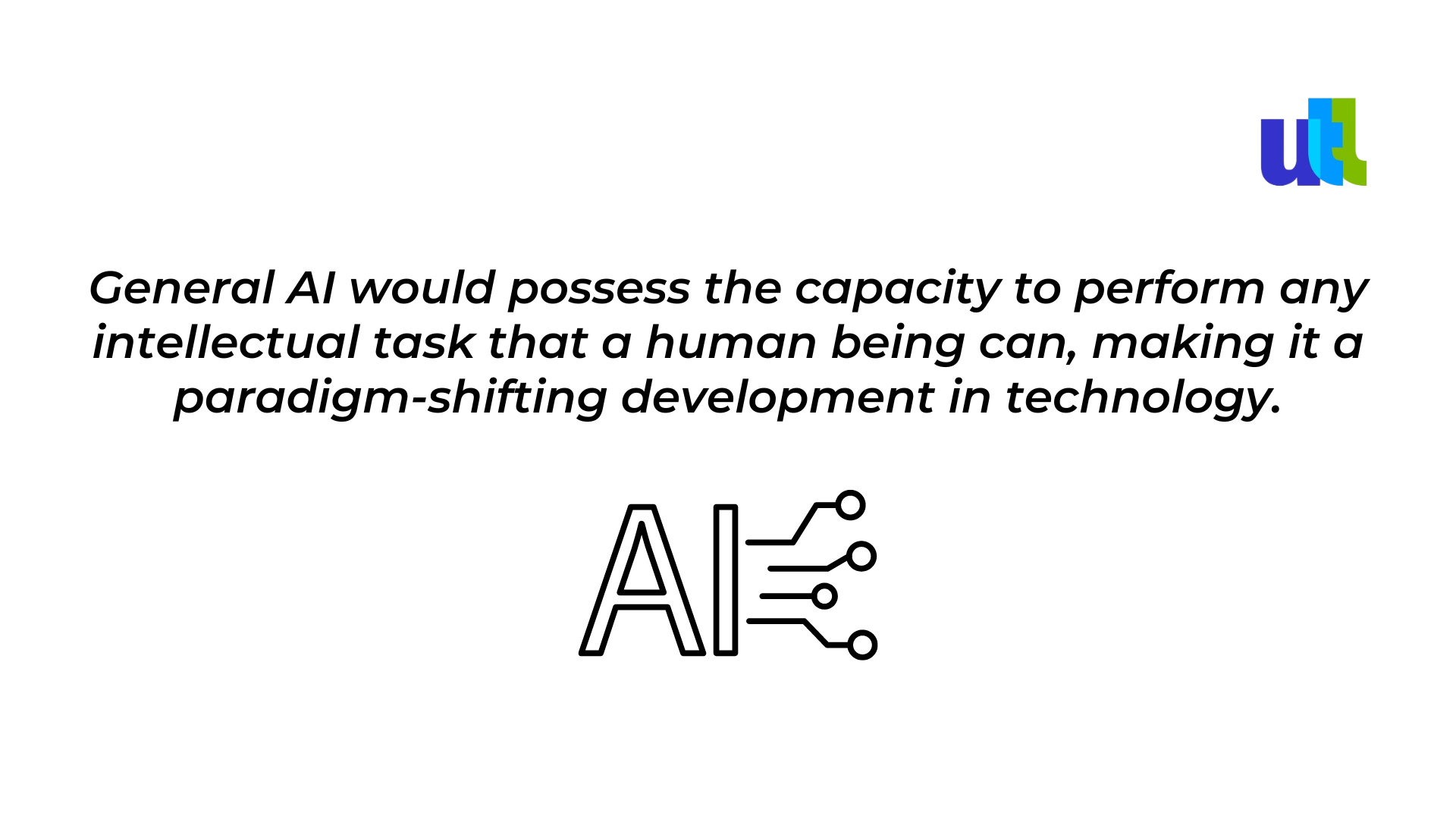
The concept of General AI, although captivating, remains largely theoretical at this point. Theoretical discussions and explorations in the field of AI ethics often revolve around the challenges and implications of creating machines with consciousness, emotions, and the potential to surpass human capabilities.
Understanding, as it's generally defined, is one of AI's huge barriers.
The type of AI can generate a masterpiece portrait but still has no clue what it has painted. It can generate long essays without understanding a word of what it has said. Achieving General AI raises profound philosophical, ethical, and technical questions that continue to fuel debates within the scientific community.
Artificial narrow general intelligence (ANGI)
Between the two extremes of Narrow AI and General AI lies the concept of Artificial Narrow General Intelligence (ANGI).
- Sometimes referred to as AGI (Artificial General Intelligence).
- Hybrid AI.
- Adaptive AI.
- Transferable AI.
“Sounds much more practical and applicable”, you might think. Indeed, ANGI is a hybrid approach that seeks to combine the depth of Narrow AI's specialization with the adaptability and flexibility of General AI. This type of AI is designed to excel in a specific domain while also being able to transfer its learned knowledge and skills to related areas.
Let’s have a look at the following examples:
- Self-Driving Cars: ANGI AI systems excel at operating within a specific domain while adapting to different scenarios. Self-driving cars can navigate roads autonomously, but they can also transfer their decision-making skills to unexpected situations like navigating through construction zones.
- Language Translation with Context: ANGI AI could translate text between languages while also understanding and preserving the contextual nuances, idioms, and cultural references that often get lost in standard machine translation.
ANGI's potential applications are vast. Imagine a medical diagnosis system that specializes in identifying certain diseases but can also extend its diagnostic abilities to new, related conditions as they emerge. ANGI systems could revolutionize industries like healthcare, finance, and manufacturing by offering expert-level performance in specific tasks while remaining capable of adapting to evolving challenges.
Superintelligent AI
At the zenith of AI evolution lies the concept of Superintelligent AI. This hypothetical form of AI surpasses human intelligence to the extent that it can outperform the best human minds in virtually every aspect of cognitive functioning.
- Often referred to as Superintelligent AGI.
- Hyperintelligent AI.
- Beyond-human AI.
- Ultra-intelligent AI.
Some of the opportunities it will offer:
- Advanced Scientific Research: Imagine an AI that can analyze complex scientific data and simulations to formulate hypotheses, design experiments, and generate breakthroughs in fields like particle physics, nanotechnology, and quantum computing.
- Global Economic Optimization: A Superintelligent AI could optimize global economic systems, balancing resource allocation, environmental sustainability, and societal well-being to create a harmonious and prosperous world.
However, the pursuit of Superintelligent AI introduces profound ethical concerns. The control and governance of a system that exceeds human intelligence raise questions about its intentions, values, and potential consequences. Ensuring that Superintelligent AI acts in the best interests of humanity becomes a daunting challenge, as depicted in popular culture through scenarios where AI becomes uncontrollable or adversarial.
Conclusion
While the primary terms (Narrow AI, General AI, ANGI, and Superintelligent AI) provide a clear framework for categorizing AI capabilities, the alternative names offer additional insights into their characteristics and potential impact on society and technology.
The journey through the spectrum of artificial intelligence is one of constant innovation, exploration, and ethical contemplation. While Narrow AI has already transformed various industries and aspects of our lives, the ultimate destination of AI's evolution remains uncertain. Researchers and ethicists grapple with questions that touch on the very nature of consciousness, creativity, and human-machine symbiosis.
As we continue to develop and deploy AI technologies, it is imperative to foster a holistic understanding of their potential impacts. The diverse types of AI remind us that technology is a tool that can be harnessed for immense good, but its responsible development and deployment require careful consideration of its implications for society, ethics, and humanity's future.
Whether we tread cautiously or embrace the possibilities, the evolution of AI promises to shape the course of human progress in ways that challenge our imaginations and redefine the boundaries of what is achievable.
For free consultation on artificial intelligence, click here.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
View the full presentation:
WRITTEN BY
Sofia Kutko
2023-08-30