In today's interconnected world, Bluetooth technology has become an integral part of our daily lives, seamlessly connecting our devices and enabling the proliferation of the Internet of Things (IoT). From our smartphones and tablets to industrial equipment, Bluetooth's pervasive presence has significantly contributed to the rapid expansion of the connected devices market. The process of effectively gathering and transmitting data to the cloud or servers is, nevertheless, a vital step in realizing the full potential of IoT solutions, even while Bluetooth makes device-to-device connection easier.
In this article, we examine a pivotal component of IoT systems—the BLE Gateway. Despite its significance, is sometimes disregarded and plays a key role in IoT networks' data handling. We will explore practical applications and clarify the role of the Gateway by illuminating its operations.
There are two main types of Bluetooth technology: Bluetooth Classic and Low Energy Bluetooth, each with a different function. The older Bluetooth Classic version excels at providing fast data transfer rates and supporting uninterrupted connections. It has uses in a variety of gadgets, especially interactive ones like wireless speakers, headphones, and in-car systems. The efficiency of Low Energy Bluetooth, on the other hand, allows for the efficient transfer of small data packets without prematurely depleting the battery of your smartphone. This eco-friendly version is perfect for gadgets like fitness trackers, medical equipment, and smart home devices where a long battery life is an important factor. Both Bluetooth versions have distinctive features that are targeted to particular use cases in our increasingly connected environment.
What is a BLE gateway?
Similar in concept to an internet router, a BLE Gateway serves as a communication channel between Bluetooth devices (such as beacons and sensors) and the Cloud/client server. Sometimes, when discussing this component, we make a distinction between the physical object and the software environment. The Gateway is especially well-suited for industrial applications because it can interact using many protocols, including WIFI, Ethernet, Bluetooth, or cellular.
How does a BLE gateway work?
The BLE Gateway will continuously scan its surroundings within a range of around 100m in order to operate and properly gather data from neighboring Bluetooth devices. The devices will periodically transmit to the Gateway to let it know they are there. To make it simple to obtain their data from the cloud or server, the Gateway will gather it in the form of frames and broadcast it on a MQTT broker.
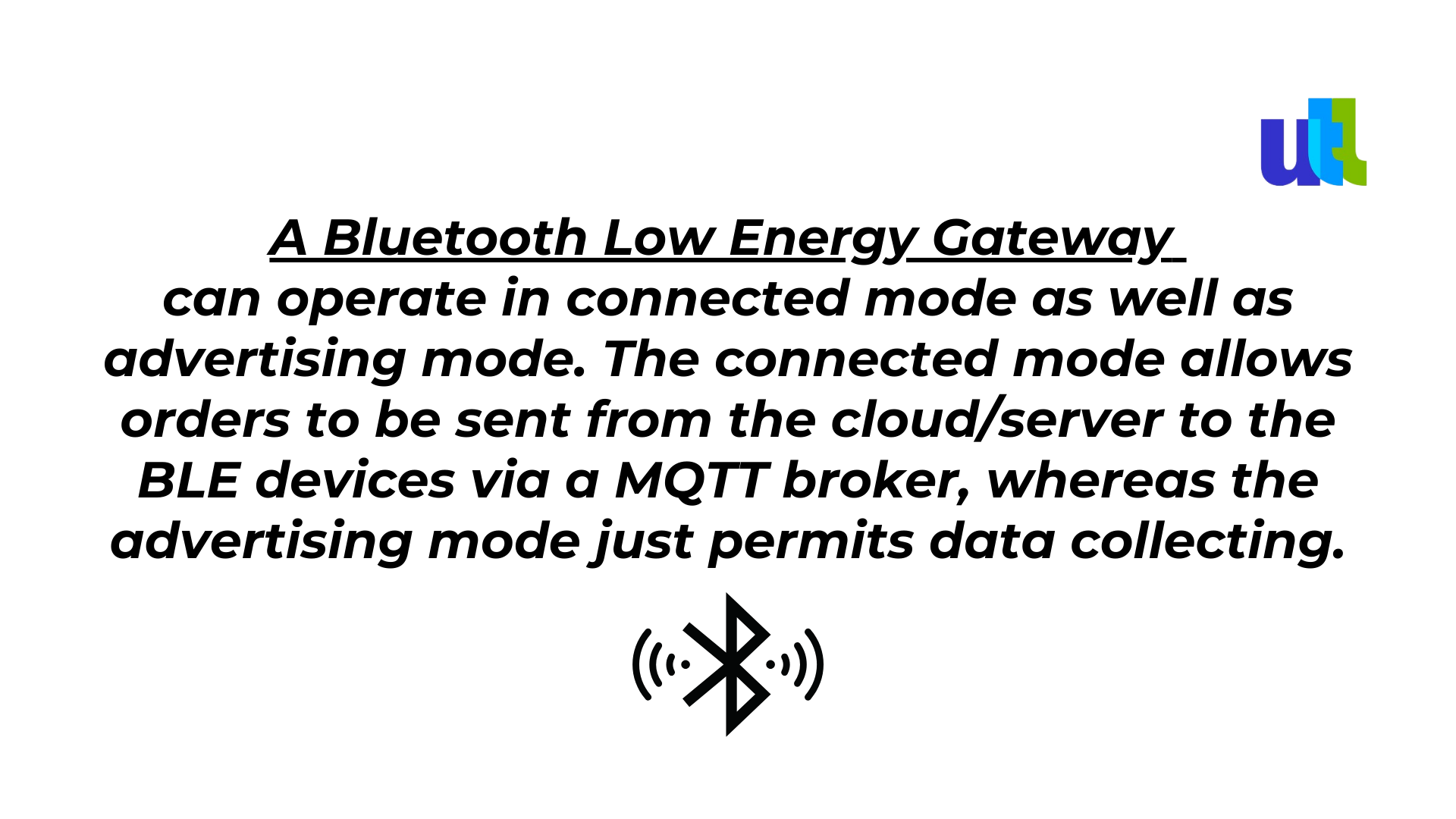
Why use a BLE gateway?

In fact, its purpose is to gather and transport the data received by Bluetooth-enabled devices in the area. A Gateway, however, is not your typical WiFi router. You can go beyond simple data transmission with some gateways, like the ELA Innovation BLE Gateway.
When compared to more established Bluetooth protocols like Bluetooth Classic and Low Energy Bluetooth, BLE-to-Cloud Integration offers a number of advantages. While BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) stands out for enabling effective data transfer with little energy consumption, Bluetooth Classic (BLE Classic) offers faster data transfer speeds and continuous connections appropriate for devices like wireless speakers and vehicle systems. Extended battery life is crucial for gadgets like fitness trackers, medical equipment, and smart home gadgets, thus this feature is very valuable. Businesses may take use of the benefits of both technologies by combining BLE with cloud-based systems, enabling seamless data exchange, real-time monitoring, and improved device management. This integration is beneficial because it not only enhances the performance of various IoT devices but also increases the overall effectiveness and dependability of supply chain activities.
Top advantages of BLE technology
Numerous benefits make Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) technology an appealing option for a variety of applications. Knowing these benefits will help you better understand why BLE is a desirable choice. We examine the key benefits of BLE technology here:
- Easy Accessibility: BLE modules are now more easily accessible than ever, making them a necessary component of everyday gadgets. Smartphones, smartwatches, TV remotes, and many other devices have BLE technology. By ensuring that BLE is widely adopted, this ubiquitous integration makes it easier to link a variety of devices.
- Low Power Requirements: BLE technology stands out for its low power requirements. This effectiveness is due to its capacity to periodically communicate data and, more importantly, to send signals only when necessary. BLE stands out from its rivals thanks to its improved power management, which guarantees increased battery life in linked devices.
- Reasonable Price: BLE technology provides affordable options for wireless connectivity. When compared to other wireless communication technologies, BLE is a more affordable alternative because of the lower cost of its parts, such as chipsets and modules. The availability of a wider range of applications is made possible by this affordability.
- Free Specifications Documents: BLE's documentation is user-friendly as well. Users can easily and at no additional cost access the relevant specification documents from the official Bluetooth website. Because of its accessibility, additional technologies or devices can be used effectively, streamlining the integration and development processes.
In conclusion, BLE technology stands out as a top option for a variety of applications due to its accessibility, low power requirements, cost-effectiveness, and easily available specifications documentation. Its relevance in the wireless communication industry is further highlighted by its capacity to effortlessly connect a variety of devices while consuming less energy. Together, these benefits show how choosing BLE might be wise for numerous industries and applications.
Top limitations of BLE technology
Despite being widely employed in numerous applications, BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy) technology has some drawbacks. Its usefulness may be impacted by these drawbacks, especially in IoT networks and applications where reliability and range are important considerations.
The short range of BLE technology is one of its main drawbacks. When devices are connected at distances more than 100 meters, BLE is unfortunately vulnerable to congestion and interference because it uses the 2.4 GHz radio range. Signal path obstructions can make this problem worse. In situations requiring long-distance communication, such as big industrial operations or outdoor settings, this limited range may present difficulties.
Another important limitation is the BLE's limited data range. BLE is less data-efficient than other wireless communication protocols, with a maximum transmission rate of only 1-2 Mbps. Due in part to the relatively long time it takes to transmit packets (about 150 milliseconds), this restriction makes it unsuitable for applications that require quick data transfer.
Beyond the inherent restrictions of BLE technology, using BLE Gateways in IoT networks poses a unique set of difficulties. These gateways have some limitations despite being useful for bridging the gap between IoT devices and the cloud. They first need a connected connection for power and internet, which might boost to the cost of the infrastructure. Including these expenses in the overall approach.
The possible vulnerability of BLE Gateways as a single point of failure within the network is still another issue. Gateways, which act as middlemen between devices and the cloud, can degrade and turn into weak points in data transfer. Deploying numerous gateways within the same network can assist ensure redundancy and lessen the impact of failures, which can help to reduce this risk.
In conclusion, it's critical to be aware of the limitations of BLE technology even though it has benefits like low battery usage and device interoperability. By comprehending it, companies and IoT professionals can adopt BLE technology in their applications and networks with confidence.
Bluetooth low energy use cases
1. Marketing
Bluetooth Low Energy has made significant inroads into marketing. The days of attracting customers solely through traditional strategies are gone. With BLE, marketers can deliver pertinent suggestions directly to users' mobile screens, effectively capturing their attention. This approach has become a popular means of engaging customers with services.
2. Retargeting Customers via Ads
BLE facilitates retargeting customers who have previously visited stores by employing different ad and marketing strategies. This approach functions similarly to platforms like Facebook or Google.
3. Indoor Navigation
Bluetooth Low Energy offers both indoor and outdoor navigation solutions. While GPS has long handled outdoor navigation, BLE now extends its benefits to indoor spaces. In malls and shopping centers, BLE-enabled smartphones provide turn-by-turn directions and highlight key landmarks along recommended routes. This functionality proves particularly valuable in multi-story stores, shopping malls, and museums, simplifying navigation and enhancing the overall shopping experience. Furthermore, BLE helps users locate nearby events and provides event details, allowing for seamless auto-check-ins and targeted event promotions.
Conclusion
Technological advancements are ongoing, and BLE has emerged as an exciting addition, enabling businesses to offer advanced experiences. In this blog, we have provided in-depth insights into Bluetooth and BLE, along with their roles in various sectors, to help you grasp the profound market transformation.
Examples of use cases employing an industrial BLE gateway
In the rapidly expanding realm of the Internet of Things (IoT), more and more companies are integrating IoT into their digital transformation efforts. While individuals typically use standard internet routers to access web applications and connect their devices, businesses are making substantial investments in advanced IoT infrastructures. Let's delve into some use cases that showcase the versatility of these technologies.
Smart building and smart office
The concept of "Smart Buildings," often referred to as intelligent buildings, has witnessed explosive growth in recent years. Industrial connected devices have played a pivotal role in this trend, as it revolves around the collection and analysis of extensive data for superior energy consumption management. To fulfill the demand for data, companies are embracing cutting-edge sensors capable of measuring a wide array of metrics, including temperature, ambient humidity, brightness, and the utilization rates of offices and meeting rooms.

Tool and parts inventory
Efficient supply chain management stands as one of the primary challenges of Industry 4.0. Manufacturers are employing automatic identification and location systems to streamline the flow of supplies and achieve real-time tracking and inventory management of tooling fleets. By affixing identifying tags known as beacons to tools and spare parts, real-time tracking of their movements becomes possible. The utilization of a BLE Gateway facilitates the recording and uploading of these movements onto a data visualization platform.
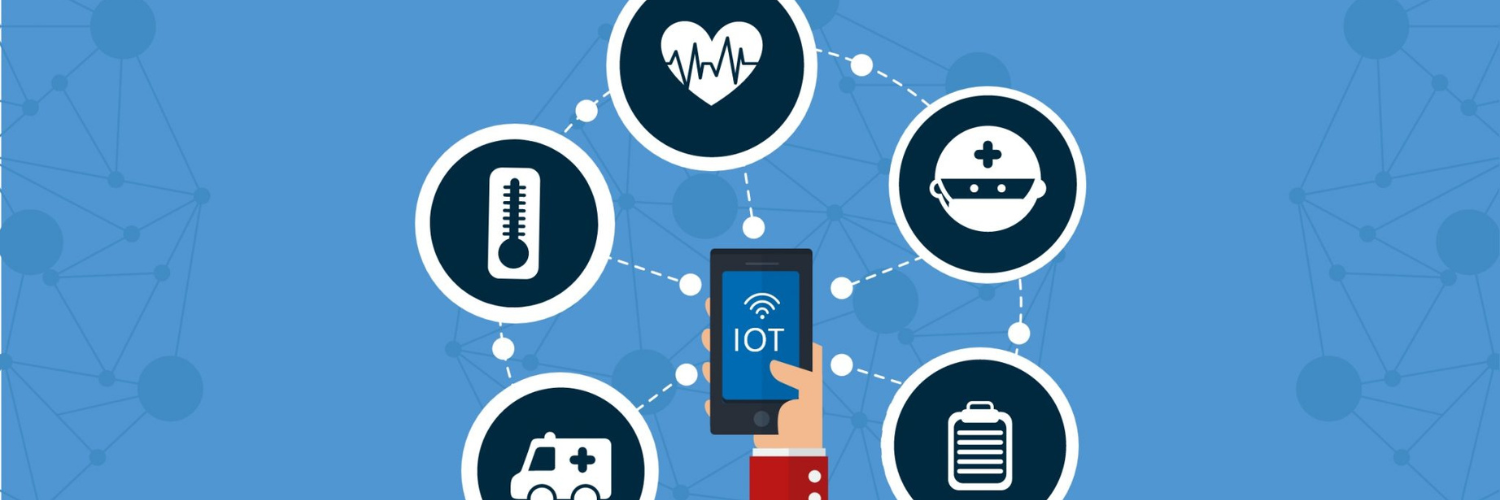
Patient monitoring in healthcare
The healthcare sector, experiencing a constant rise in hospitalizations, places paramount importance on hospital performance improvement. Many hospitals are turning to connected solutions to enhance the patient journey. By employing beacons for patient identification, seamless transmission of patient records between different departments is facilitated, minimizing data loss. Furthermore, beacons can aid in patient location within hospitals, simplifying navigation for patients, reducing appointment delays, alleviating waiting room congestion, and optimizing patient flows.
However, to ensure a seamless experience for both patients and hospital staff, the establishment of an efficient and secure infrastructure is imperative. Given the potential for a high volume of Bluetooth beacons, deploying multiple Gateways is recommended to streamline data transmission to client servers.
Conclusions
In conclusion, the benefits of BLE-to-Cloud integration are significant in today's interconnected world. While Bluetooth technology has become ubiquitous in our daily lives, its full potential in IoT solutions is realized through the efficient gathering and transmission of data to the cloud or servers, a role played by the often-overlooked BLE Gateway.
The BLE Gateway acts as a crucial communication channel between Bluetooth devices and the cloud/client server, making it particularly suited for industrial applications with its ability to interact using various protocols, including WIFI, Ethernet, Bluetooth, or cellular.
In summary, BLE technology offers numerous advantages, such as easy accessibility, low power requirements, affordability, and readily available documentation. However, it does come with limitations, particularly in terms of range and data efficiency. Understanding both its strengths and weaknesses allows for informed decisions when implementing BLE in various applications and networks. Bluetooth Low Energy continues to play a pivotal role in technological advancements, shaping the way businesses and individuals connect and interact in our increasingly digital world.
For free consultation on BLE-to-cloud integration, click here.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
View the full presentation:
WRITTEN BY
Milda Butkeviciute
2023-09-27