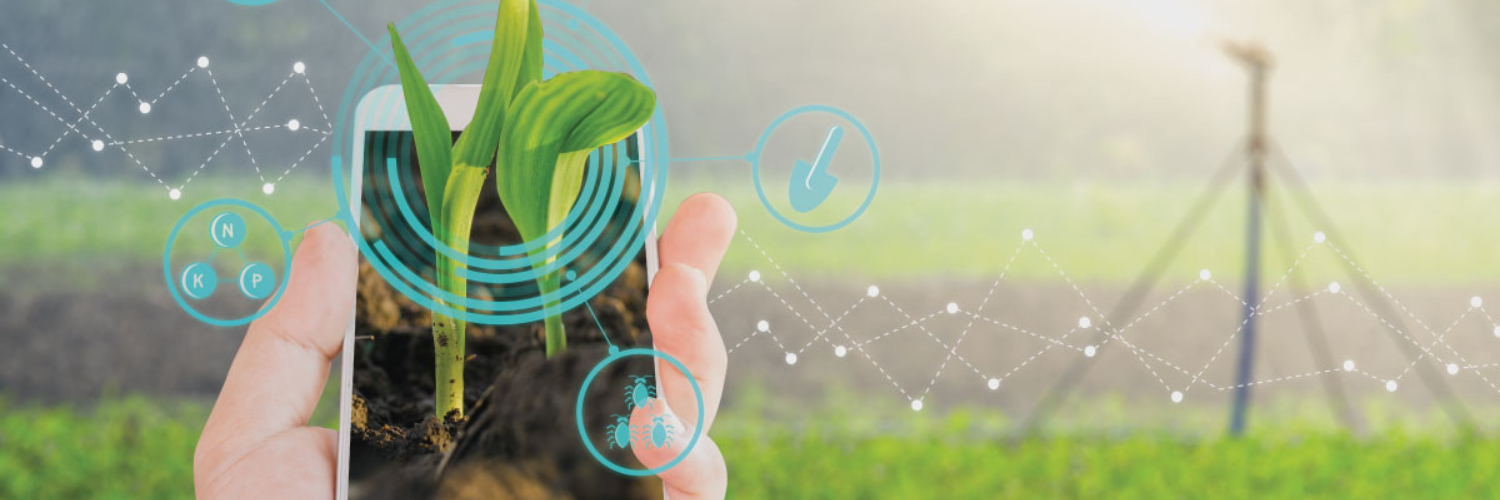
With the global population steadily increasing and environmental challenges on the rise, the agricultural sector is under pressure to produce more with fewer resources while minimizing its ecological footprint. In this article, we will explore the profound impact of IoT on agriculture and how it is helping us cultivate a more sustainable future.
In a world grappling with the challenges of a growing population, climate change, and resource scarcity, agriculture stands at the intersection of innovation and necessity. The Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a transformative force in the sector, paving the way for new and efficient farming practices.
The global challenge
With the global population expected to exceed 9 billion by 2050, the demand for food is rising at an unprecedented rate. Agriculture must evolve while facing the harsh realities of climate change, diminishing arable land, and depleting natural resources.
Traditional farming practices, often reliant on guesswork and manual labor, are increasingly inadequate to meet the growing demand for food, fiber, and biofuels. Furthermore, climate change, water scarcity, and soil degradation threaten the stability of agriculture. In this context, IoT offers a lifeline for the industry.

IoT's role in agriculture
IoT in agriculture involves the integration of sensors, data analytics, and automation to monitor and manage various aspects of farming operations. Here are some ways IoT is reshaping agriculture:
Precision agriculture
IoT sensors collect data on soil moisture, temperature, nutrient levels, and weather conditions. Farmers can use this data to make precise decisions about irrigation, fertilization, and pest control, optimizing resource use and increasing yields.
Livestock monitoring
IoT-enabled wearables and sensors track the health and well-being of livestock, providing early warning signs of illness and improving animal welfare.
Water management
Water is a precious resource. IoT devices help farmers optimize irrigation practices by delivering insights into soil moisture levels and weather conditions. Smart irrigation systems can automatically adjust water flow based on real-time data, minimizing wastage and conserving water resources.
Crop management
Drones equipped with IoT technology can survey fields, identify crop diseases, and assess overall crop health. Machine learning algorithms detect the very first signs and help to react timely. IoT sensors can monitor conditions in storage facilities, such as temperature and humidity, ensuring the long-term quality and preservation of crops.
Energy management
IoT technology can optimize energy usage on farms. This includes monitoring energy consumption in machinery and facilities, leading to cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
Smart pest control
IoT devices can monitor and identify pest populations in real-time. This information allows farmers to implement targeted pest control measures, reducing the need for broad-spectrum pesticides. Check the examples of Utah Tech Labs’ pest control solutions (https://www.utahtechlabs.com/field-service-management)
Supply chain optimization
IoT devices are used to monitor the condition of agricultural produce during transportation, ensuring that food reaches consumers in the best possible condition and reducing food waste.
Sustainable farming
IoT can help farmers reduce their environmental footprint by optimizing resource usage, minimizing water and energy waste, and adopting eco-friendly practices.
By harnessing the power of real-time data and smart decision-making, farmers can reduce resource consumption, increase yields, and produce higher-quality crops and livestock. However, to unlock the full potential of this data, it often requires rapid and localized processing – a challenge traditionally addressed by edge computing.
The rise of edge computing
Edge computing shifts the computational power and data processing closer to the source of data generation, which is often at the "edge" of the network, near the IoT devices themselves. This shift addresses several critical challenges in the IoT ecosystem. What does it mean for agricultural and other industries?
- Reduced latency
Edge computing significantly reduces data transfer times, making real-time processing and decision-making possible. This is vital for applications like autonomous agricultural machines, where speed of reaction is extremely important.
- Connectivity in rural areas
Agricultural operations often extend into remote and rural areas where reliable internet connectivity can be a challenge. Edge computing thrives in such environments by processing data locally, minimizing the dependence on constant internet access. This enables farms in remote locations to benefit from IoT technologies without connectivity concerns.
- Enhanced security
By processing data locally, edge devices can minimize exposure to potential security threats. Rather than transmitting sensitive data to remote servers for analysis, edge devices keep data on the farm, reducing the risk of data breaches and ensuring that farmers retain control over their proprietary information.
- Bandwidth optimization
Edge computing reduces the strain on network bandwidth by filtering and processing data locally. It also lowers the cost associated with transmitting vast amounts of data to centralized servers.
- Improved reliability
Decentralized processing means that even if one edge device fails, others can continue to function independently, ensuring system reliability.
The convergence of IoT and edge computing in agriculture is revolutionizing the industry by providing farmers with the tools they need to transform traditional practices into data-driven, efficient, and sustainable operations.

Famous success stories
Several real-world examples showcase the potential of IoT in agriculture:
The John Deere Precision Agriculture system uses IoT sensors to guide tractors, adjust planting, harvesting operations, and optimize fuel usage, leading to increased crop yields and reduced costs.

The "Connected Cows" project in the Netherlands employs IoT technology to monitor the health and behavior of dairy cows, with the aim of improving the quality of their milk production and animal welfare.
Companies like IBM's Watson Decision Platform for Agriculture offer data-driven insights to farmers, helping them make informed decisions about planting, harvesting, and pest control solutions.
These IoT applications not only enhance the efficiency and productivity of agriculture but also contribute to sustainable and environmentally responsible farming practices by reducing resource waste, minimizing chemical usage, and improving overall resource management.
Conclusion
The integration of IoT in agriculture is not just a technological advancement; it is a necessity for a sustainable future. Edge computing's ability to process data locally in real time is a fundamental shift that empowers farmers to optimize resource use, reduce waste, and increase crop and livestock yields.
By harnessing the power of data and automation, farmers can deliver more products with fewer resources, with less environmental impacts, and adapt to the challenges posed by a changing climate situation much easier.
As IoT continues to evolve, so will the agricultural industry, cultivating a brighter and more sustainable future for generations to come.
For free consultation on IoT's role in agriculture, click here.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
View the full presentation:
WRITTEN BY
Sofia Kutko
2023-09-11