When you start considering a product idea, it can be overwhelming because you want to do everything at once to develop a fully functional product before entering the market. The challenge lies in time and funding. If your development cycle is too lengthy, the product may lose its relevance. Meanwhile, funding is often limited as well. Here are seven practical strategies to lower development costs while upholding high standards and achieving a quick market entry path:
1. Prioritize Core Features
- Focus on must-have features that drive user value rather than adding unnecessary functionalities.
- Use a phased rollout to introduce enhancements over time based on user feedback.
2. Leverage Open-Source & AI agents
- Utilize established open-source libraries and frameworks to reduce development time and costs.
- Avoid reinventing the wheel by leveraging community-supported solutions.
- Use a team that knows how to use generative AI to code fast.
3. Implement Agile & Lean Development Practices
- Work in iterative sprints to maintain flexibility and avoid wasting effort on unnecessary features.
- Validate assumptions early through prototyping and MVP testing.
- Take every possible iteration to your audience or alpha users to get the market validation. Do not wait too long.
4. Optimize Development Team Structure
- Do not try to hire in-house in the first place. Managing a development team is a big deal. The bigger problem is that a domain expert team has been doing this job for a long time, and they have an internal support system when they are stuck. They have cross functional and cross-project teams to support each other. You can't create the entire infrastructure in a short time. Hiring an in-house team is a better idea when you start seeing some product success.
- Assign specialized roles to improve efficiency and prevent bottlenecks.
5. Automate Testing & Deployment
- Use CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment) pipelines to streamline development.
- Automate testing to catch bugs early and reduce manual labor costs.
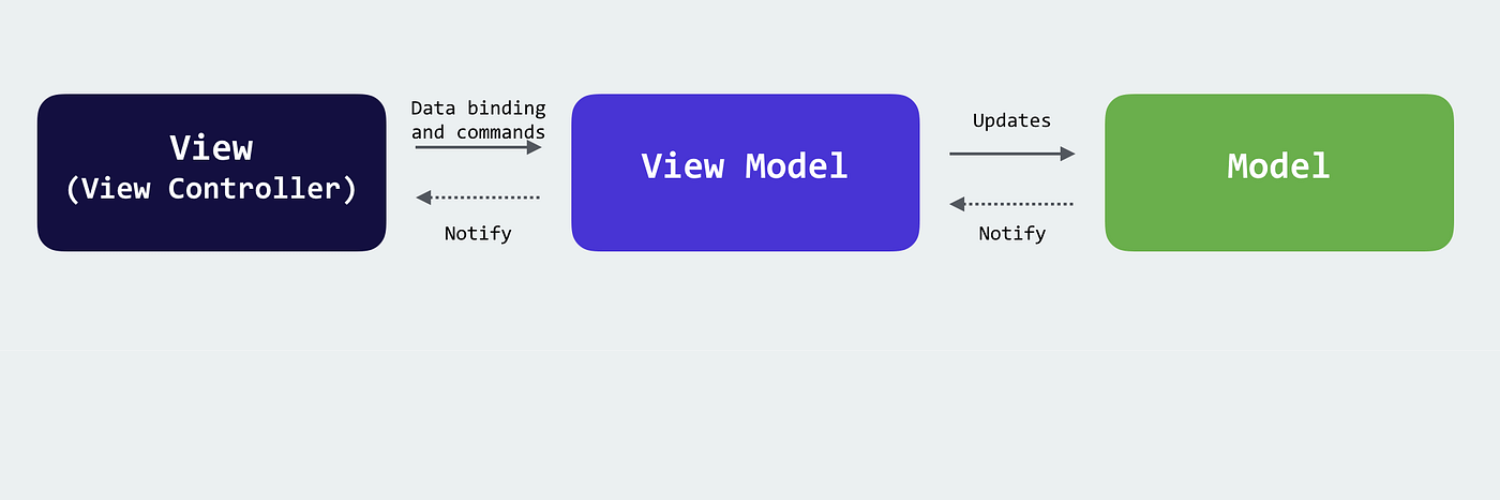
6. Reuse Code & Modular Development
- Build reusable components that can be adapted for different parts of the product.
- Utilize microservices architecture to scale individual functionalities as needed.
7. Monitor & Optimize Resource Usage
- Use cloud services strategically to scale infrastructure based on demand.
- Regularly audit software performance to identify and eliminate inefficiencies.
Conclusion
Reducing development costs doesn’t mean compromising on quality. By making strategic choices—prioritizing core features, leveraging open-source tools, and optimizing development workflows—businesses can maintain high standards while staying within budget. Combined with a phased development approach, these strategies help ensure sustainable growth and long-term product success.
WRITTEN BY
Deimante Boguzaite
2025-03-31