Field service management (FSM) is a critical function for businesses that rely on service operations, such as maintenance, repairs, installations, and inspections. Efficiently managing field service operations is essential for customer satisfaction, cost control, and maintaining competitive advantages. Integrating Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) into FSM processes is a strategic move that offers numerous benefits by streamlining operations, improving asset performance, and enhancing overall customer experiences.
Field Service Management (FSM) has come a long way from its origins as a simple dispatching system. In today's fast-paced business environment, it plays a pivotal role in ensuring efficient field operations, delivering top-notch customer service, and driving business growth…
But what about its challenges?
The complexities of today's field service
While technology and data-driven practices offer ways to enhance efficiency and customer satisfaction, organizations should also be prepared to address some of the most common issues, including:
- Customer expectations
Today's customers expect seamless and personalized service experiences. Thus, FSM must facilitate real-time communication, appointment scheduling, and service tracking to meet these expectations.
- Technological advancements
Modern FSM solutions are expected to leverage all the cutting-edge technologies like IoT, AI, and mobile apps.
- Remote work and collaboration
With the rise of remote work, FSM tools are expected to be cloud-based, facilitate collaboration and data sharing between in-house teams and field technicians.
- Data-driven decision-making
In case of FSM, Data analytics is completely crucial for improving operations and customer service. A good FSM solution is expected to identify trends, optimize routes, and make strategic decisions; mostly automatically.
What is EAM? And how can it help?
The history of EAM can be traced back several decades, with its development closely tied to advancements in technology and changes in business practices. In the 1970s and 1980s, the advent of computer technology led to the creation of the first CMMS. These systems were initially focused on tracking and scheduling maintenance tasks and work orders, allowing organizations to transition from paper-based methods. That was a huge step, but nothing compared to today’s advancements.
Later, as technology continued to evolve, CMMS systems expanded their capabilities beyond maintenance management. They started incorporating asset tracking, procurement, inventory management, and other features - for more comprehensive EAM solutions.
Today, enterprise asset management (EAM) is a combination of software, systems and services used to maintain and control operational assets and equipment. However, the initial aim of the invention was to optimize the quality and utilization of assets throughout their lifecycle, increase productive uptime, and reduce operational costs.
EAM is a holistic approach to managing an organization's physical assets throughout their lifecycle.
It involves work management, asset maintenance, planning and scheduling, supply chain management and environmental, health and safety (EHS) initiatives.
In recent years, cloud-based and mobile EAM solutions have become increasingly popular. These solutions offer scalability, flexibility, and the ability to access EAM data from anywhere, making them well-suited for modern businesses with distributed operations.
What is the difference between EAM and CMMS today?
EAM is often associated with a computerized maintenance management system (CMMS), but a closer look at both reveals they are different. As was described previously, CMMS can be one aspect of EAM. Historically, it mainly focuses on centralizing information to facilitate and automate maintenance management processes; while EAM is an asset lifecycle management approach that supports asset performance from acquisition to disposal.
Why Is EAM becoming so popular?

At its core, EAM involves the systematic management of an organization's assets throughout their entire lifecycle. Assets in this context can encompass a wide range of physical items, including machinery, equipment, vehicles, facilities, and even IT infrastructure. EAM is a vital tool for businesses looking to stay ahead of the curve, and here is why:
1. Improved operational efficiency
EAM streamlines operations by ensuring that assets are available, well-maintained, and utilized optimally. This reduces downtime, enhances productivity, and minimizes costly disruptions.

2. Unplanned costs reduction
By proactively managing assets and implementing preventive maintenance strategies, organizations can extend the lifespan of their assets and reduce unplanned repair and replacement costs.
EAM integration helps FSM teams manage spare parts and inventory efficiently.
3. Regulatory compliance
EAM helps companies comply with industry regulations and safety standards, reducing the risk of penalties and legal issues. It does a huge part of legal work.
4. Data-driven decision making
EAM systems collect vast amounts of data on asset performance and maintenance history. This data can be analyzed to make informed decisions about asset investments, upgrades, and replacements.
5. Enhanced safety
In fact, regular maintenance and inspections of assets reduce the likelihood of accidents and injuries, creating a much safer working environment.
FSM customers appreciate quick issue resolution and proactive maintenance that minimizes disruptions.
6. Improved asset performance
The technology allows organizations to track and optimize asset performance. Predictive maintenance, enabled by technologies like IoT and AI, helps identify potential issues before they become critical.
In fact,…
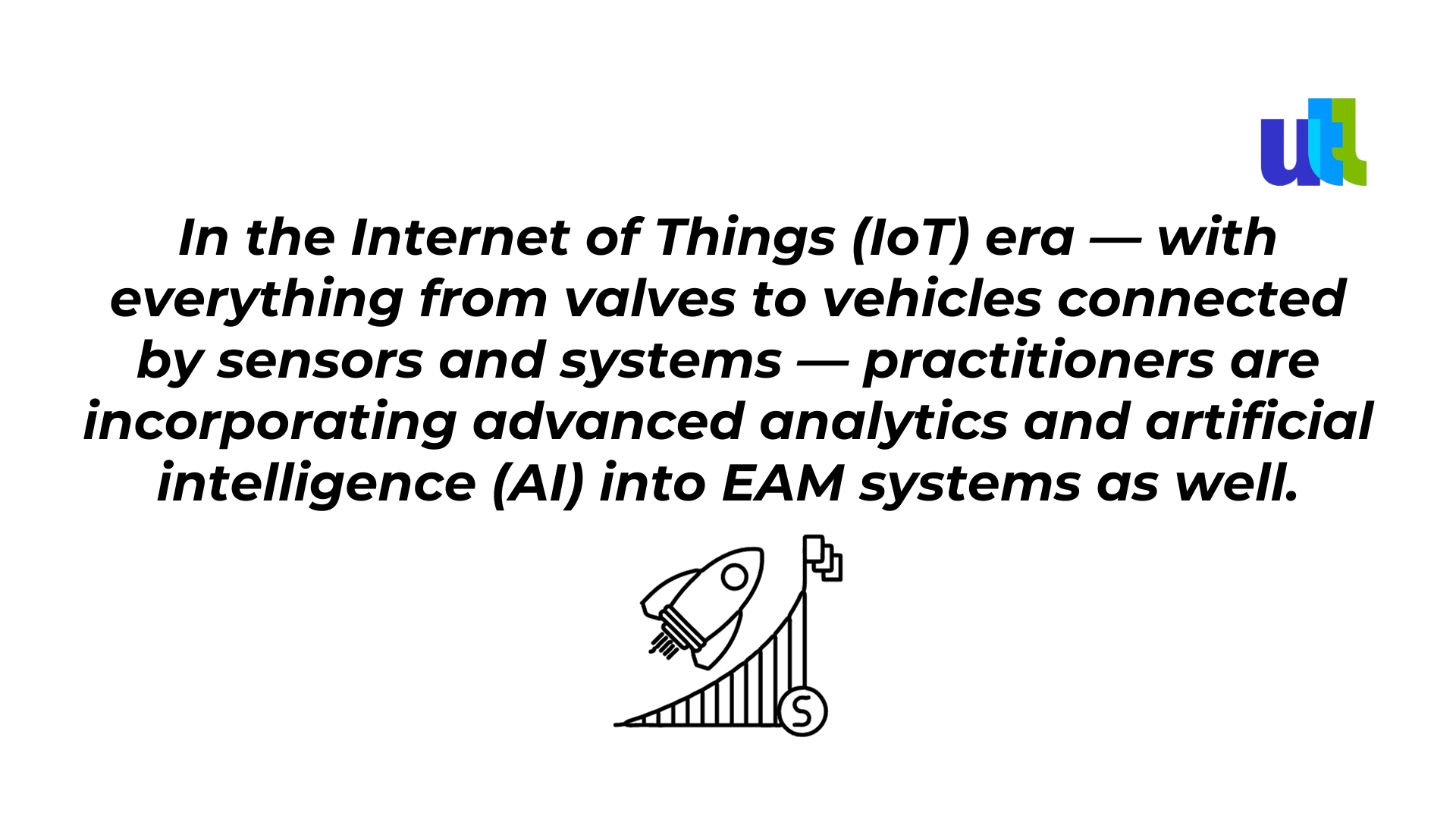
How do they work together?
Data gathered from instrumented assets is analyzed using AI techniques. The resulting insights help maintenance teams make better decisions, enhance efficiency, perform preventive maintenance, and maximize investments in their physical assets.
Meanwhile, the proliferation of smartphones and tablets has led to the vast use of EAM mobile apps that empower field technicians to access asset information, perform inspections, and update work orders in real time, increasing efficiency and accuracy.
To conclude
Modern field service management is marked by both unprecedented opportunities and challenges. However, by proactively identifying and addressing those challenges, businesses can ensure their FSM operations remain agile, adaptable, and equipped to deliver exceptional service. Especially in today's dynamic business landscape.
The integration of Enterprise Asset Management (EAM) into Field Service Management (FSM) is a strategic move that empowers businesses to optimize their field service operations. It enhances asset visibility, enables predictive maintenance, streamlines work order processes, and ultimately leads to improved customer satisfaction and cost reduction. Today, EAM has evolved into a sophisticated discipline, driven by data analytics, artificial intelligence, and IoT technology - all working together.
Utah Tech Labs professionals believe the synergy between EAM and FSM is set to become even more critical for businesses looking to stay competitive and deliver exceptional service in an increasingly demanding and dynamic marketplace.
For free consultation on field service management, click here.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
View the full presentation:
WRITTEN BY
Sofia Kutko
2023-09-25